For more than a decade, the DIY world has experimented exponential growth thanks to the introduction of the popular Arduino boards. These boards changed the way makers develop their projects, making this process much easier, which is the main reason why they became so popular.
Arduino was created under the free hardware and software concepts, which generates collaboration between all users, the main reason why its community has not stopped growing and there are so many libraries in this environment.
Despite the acceptance of these boards based on Atmel microcontrollers, since 2016 there is a very interesting alternative that has been gaining territory due to its favorable characteristics more than anything else for the Internet of Things. With this article we will introduce the main features of these interesting boards and we will compare them with the popular Arduino boards.
ESP8266
The ESP8266, core of the boards that we will see below, is not a microcontroller, it is a SoC (System on Chip) that includes a 32-bit RISC microcontroller that works at 80 MHz with integrated WiFi connectivity. This SoC can be used as an application controller and as a WiFi module to be used from another device through the UART or I2C interfaces, such as an Arduino board.
To store data and firmware, it contains an external flash memory that can be up to 32 MB, although the available boards vary from 512 KB to 4 MB, which allows us to work with databases without using external storage modules.
Applications such as monitoring sensors and operating actuators from our browser are easier with this device due to its communication and storage capabilities. As if this were not enough, it is very useful in projects that are powered by batteries due to its sleep mode, which greatly reduces the consumption of the SoC. Next we will see two of the main boards based on this SoC:
ESP01
This is one of the most famous boards based on ESP8266 due to its small size and low cost. Its main disadvantage is that it has very few accessible pins available, only 8, being two for power. The other one is related to prototyping, and is that it is not compatible with standard breadboards.
Despite these disadvantages, it is the most used board if you want to use it as a WiFi module to be controlled through the I2C or UART interfaces, and due to its great acceptance, special modules have been developed for this board such as the relay module or DHT module.
| DHT Module | Relay Module |
|
|
NodeMCU
This is probably the most famous board in the ESP8266-based family. It has an integrated 3.3V regulator, reason why it can be powered at 5V, the same USB-Serial converter that most Arduino boards bring, the CH340G and generally have a 4 MB flash incorporated, which is more than the 1 MB flash that ESP01 generally incorporates.
| NodeMCU |
Arduino Board
Arduino boards are based on ATMEL microcontrollers. Most of them like Arduino Nano, Uno and Mega are 8 bits boards. These boards works at 16 MHz, leaving a lot to be desired compared to the 80 MHz of the ESP8266, not to mention that the microcontroller of this SoC is 32 bits. The exception to this rule is the Arduino Due, presenting itself as the most powerful board in the family, it works at 84 MHz and has a 32-bit microcontroller, but due to its price it is not very popular. For this reason, the board chosen for our comparison is the Arduino Mega, presenting itself as the most ‘powerful’ of the popular ones.
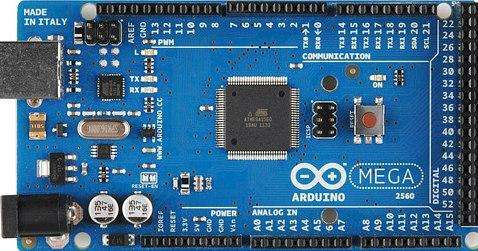
Arduino Mega
This board is based on the AtMega 2560 and the reason it is so attractive is because of its extensive GPIO (General Purpose Input Output). Like most boards in the family, it has its own USB-Serial converter and can be powered with a USB cable, making it ideal for prototyping projects and very convenient for makers. One of its main characteristics is that it has 4 UART ports, not very useful at present, but each project has its peculiarities. In addition, this board has a large number of analog inputs, as well as digital inputs and outputs. We will go into details regarding this in the next section.
| Arduino Mega |
Comparison
| Board | Price | Voltage Input | Wireless Conectivity | Sleep Mode | Storage | Processor | Digital Input/Output | Analog Inputs |
| ESP01 | $ 1 – $ 5 | 3.3 V. It can only be powered through the Vcc pin | Integrated WiFi | Available | External Flash 512 KB – 1 MB | 32-bit microcontroller @ 80 MHz (160 MHz overclocked) | 4 | Not available |
| NodeMCU | $ 2 – $ 6 | 5 V. Can be powered through any Vcc pin and USB port | Integrated WiFi | Available | External Flash 4 MB | 32-bit microcontroller @ 80 MHz (160 MHz overclocked) | 13 | 1 (10 bits) |
| Arduino Mega | $ 9.59 – $ 15 | 5 V. It can be powered through any Vcc pin and a USB port. It also has a 7 – 12 V power input | Only through external modules | Available but not with the same features as ESP | EEPROM 4 KB | 8-bit microcontroller (AtMega 2560) @ 16 MHz | 54 | 16 (10 bits) |
Selection
There are many variables to consider to select one of this boards, but it mainly depends on the project. Obviously of the boards exposed here, the most suitable for a project that requires interacting with lot of peripherals is the Arduino Mega, mainly due to its extensive GPIO. Despite this, it is not common to use too many inputs and outputs of a microcontroller in a project. Anyways, we can always use an I2C port expander, this will be explained in a later post.
On the other hand, boards based on the ESP8266 present a better performance in terms of processing capacity, not to mention the benefits it offers related to connectivity, storage and energy saving. Regardless of these advantages, the main advantage of boards based on the ESP8266 is their price, which is the main reason why it has become so popular with makers. Nowadays, many makers have started using ESP8266-based boards because they are much more feasible for projects related to the Internet of Things, where the trend is to use wireless communications.
We would like to know your opinion about this article and how useful it was, let us know on the comments below. If you think it’s worth sharing it, follow us on our social networks and subscribe to our YouTube channel where we will be launching content soon. Remember to subscribe to our Newsletter to be aware of all our publications and information.