In the previous article we made a comparison between two of the more popular LPWANs (Low Power Wide Area Networks): LoRaWAN and SigFox. In this article we will follow a fairly similar trend, but we will compare two LPWANs that, unlike the two compared in the previous article, operate on licensed spectrum, these are: NB-IoT and LTE-M.
Introduction
NB-IOT and LTE-M are protocols for low-bandwidth cellular communications that connect devices that need to transmit small amounts of data at low cost (both in terms of hardware and subscription) and with a long battery duration
The goal is to create devices of small size, low energy consumption, low cost and high connectivity through infrastructure and underground. The combination of these features results in devices that can be used in applications that were previously impossible to develop due to cost.
Advantages of NB-IOT and LTE-M
Low power consumption and extended range
Battery life is increased by reducing communication between the device and the network. For this, the devices can go into sleep mode or reduce the time through which they communicate with the network. Both NB-IoT and LTE-M offer better coverage than 4G through infrastructure or underground.
Applications that require a quick response or poor coverage are less likely to extend battery life. Due to this, applications that require a life cycle of 10 years must be deployed in areas with good coverage. To create a balanced response in terms of battery usage and improved coverage, different techniques are used. These can be sleep mode and apply an adequate poll time to the network.
New pricing models
Pricing models for NB-IoT and LTE-M will differ from traditional pricing for telecommunications services. This is due in large part to the difference in traffic when it comes to the Internet of Things. In other words, there will be a large number of NB-IoT and LTE-M devices connected, but they will send small amounts of data.
Instead of the per-device data usage pricing model, network providers will likely consider charging access fees to devices. Another possibility is a price model based on the two mentioned, to better adapt to the network resources consumed by these devices.
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
NB-IOT was conceived to enable efficient communication and long battery life for massively distributed devices, and uses the existing mobile phone network to connect these objects. Next we will comment on its main characteristics:
- Low cost: NB-IOT modules have lower cost than those of other communication technologies including LTE-M. From the user’s point of view, it is important to underline that the subscription cost will be cheaper than current communications.
- More cell phones per antenna: NB-IOT devices use a 180KHz bandwidth and it is estimated that each network can fit 100,000 connections.
- Excellent penetration indoors and underground.
LTE-M (Long Term Evolution for Machines)
LTE-M, also known as CAT-M1, uses installed LTE antennas and is optimized for higher bandwidth and for mobile connections that include voice. Let’s look at the three things to look for when we talk about LTE-M:
- Upload and download speed: Up to 1Mbps, being much higher than the speeds offered by NB-IoT.
- VoLTE (Voice over LTE):This technology allows the transfer of voice.
- Mobility: It is prepared for devices on the move.
Comparison LTE-M and NB-IOT
| NB-IoT | LTE-M | |
| Band width | 180 KHz | 1.4 MHz |
| Maxium data rate | < 100 | 384 Kbps |
| Download / Upload speed | 27.2 / 62.5 Kbps | Until 1 Mbps |
| Latency | 1.5 – 10 s | 50 – 100 ms |
| Battery life | + 10 years depending on the use case | 10 years depending on the use case |
| Energy consumption | Better at low transfer speeds | Better at medium transfer speeds |
| Frequency deployment | Flexible | Only in LTE |
| Indoor penetration | Excelent | Good |
| Voice transmission | No | Yes, through VoLTE |
Main aspects to highlight
Below we discuss the main aspects of these LPWANs:
- Both LPWANs present better coverage through infrastructures or underground than LTE, with NB-IoT being the LPWAN that presents better performance in this regard.
- NB-IoT modules can be deployed in both 3G and 4G frequencies, while LTE-M can only be deployed in 4G frequencies.
- NB-IoT modules have a lower cost than LTE-M modules.
- LTE-M is a better alternative for moving devices.
- For voice transmission, LTE-M is the only option available thanks to VoLTE.
- LTE-M features very low latency, making this LPWAN ideal for use cases where fast response is required.
Despliegue
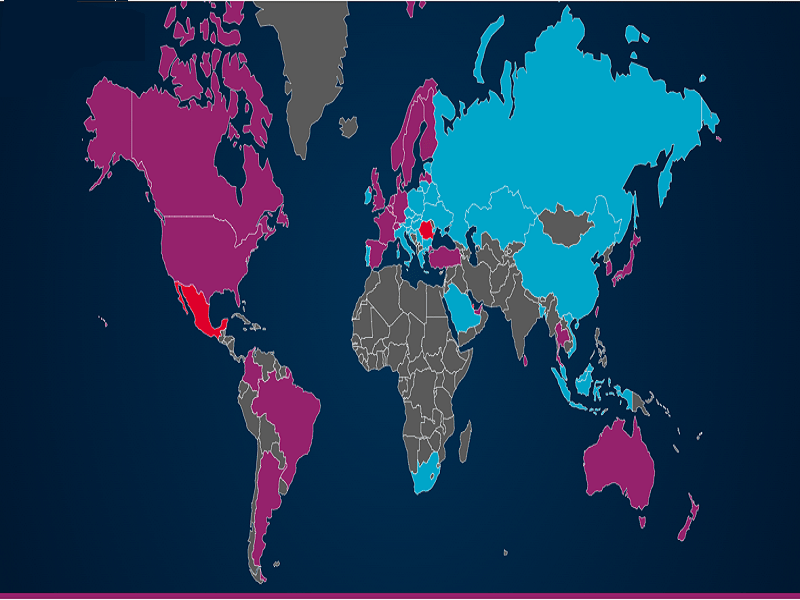
The image above shows the current expansion of these two technologies. The purple color represents the areas where there is support for both technologies, the blue color where there is only support for NB-IoT and the red color the areas where only LTE-M is available.
Conclusiones
As we have shown, there are numerous factors to consider when selecting one of these LPWANs that operate on licensed spectrum. NB-IoT is generally used in applications where long battery life is required and LTE-M capabilities such as VoLTE are not required.
If you liked our article, give it a “like”, comment and share on your social networks. Subscribe to our Newsletter so that you are aware of the latest news. We have a very active Facebook community, very interesting post Instagram and you will find constant activity on our Twitter.




