In the previous article we gave an introduction to LPWANs (Low Power Wide Area Networks) and we saw that with the increase in Internet of Things applications, the use of these networks has increased dramatically in recent years. In this article we will present the main unlicensed implementations of these networks and their characteristics.
Different implementations
LPWAN technologies can be divided into unlicensed spectrum such as Sigfox and LoRa, and licensed spectrum such as Long-Term Evolution Cat-M1 (LTE-M) and NarrowBand IoT (NB-IoT). In this article we will focus on Sigfox and LoRa, whose implementations operate on unlicensed spectra. The difference between these classifications is dependent on the frequency spectrum in which the LPWAN operates, generally those that belong to licensed spectrum operate on frequencies used by operators to provide 3G or 4G telephone service.
LoRaWAN
The LoRaWAN protocol is an open standard operating in the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) frequency spectrum. This spectrum is between 863 and 870MHz in Europe and between 902 and 928 MHZ in the United States. It is designed to use an extended star topology, where end devices are connected to gateways and these, in turn, are connected through typical IP networks.
To use this technology to communicate IoT devices, there are two alternatives:
- Create your own network
-
It will be necessary to buy the LoRa chips and develop your own gateways and nodes. In addition to creating your own network, it will be necessary to carry out maintenance and keep all the necessary software updated. As an advantage, the user will be able to adjust and adapt this network to their needs.
-
- Use a network operator
- Currently, several operators are starting to offer LoRaWAN networks in certain areas, such as Orange. In this way, connectivity plans can be contracted with these companies, thus avoiding network maintenance. This option has the disadvantage that the operator may stop offering this service in a few years.
Architecture
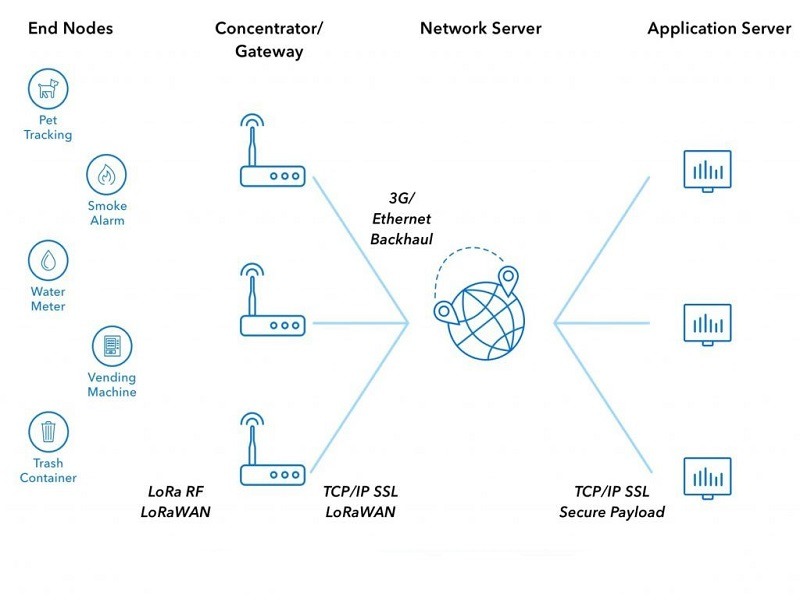
In the previous image we can understand how a LoRaWAN network works. The communication between the end devices and the gateways is through the LoRaWAN protocol based on radio frequency. Each of these gateways has an IP address assigned by the network server to which they are connected. This can be assigned via a WiFi network, Ethernet or a cellular network. Then each of our applications communicates with this server through any of the methods mentioned above thanks to the IP addresses.
Behind this protocol is Lora, a non-profit association. Currently, there is no standardized or dominant protocol for LPWAN networks, and that is what this alliance seeks to change. In the LoRa Alliance we can find some technological giants such as Alibaba, Cisco, IBM, Charter Communications and SoftBank.
SigFox
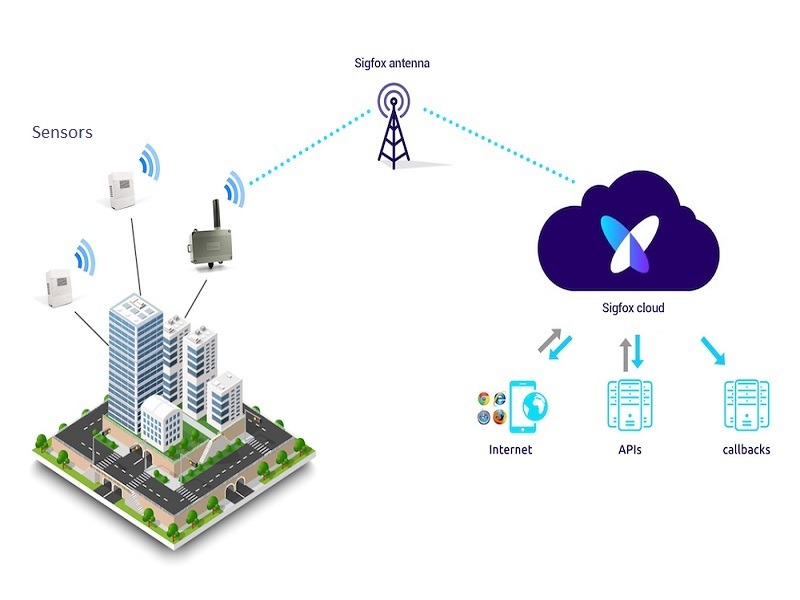
SigFox is a French company that aspires to become the first global IoT network provider. It features narrow-band technology that operates in the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) frequency spectrum: 868MHz in Europe and 902MHz in the United States.
The company deploys its antennas with the help of local telecommunications companies around the world. Currently the network is present in 70 countries, covering more than one billion people and 5.2 million square kilometers.
In the data delivery section, SigFox imposes a series of limitations on the messages transferred through the network, where each device can send only 140 messages per day with a limit of 7 messages per hour. Each message can be up to 12 bytes in length. The radio modules can also receive 4 incoming transmissions per day.
SigFox fully manages the communication between the IoT device and the cloud, which makes the integration of the radio module a fairly simple process for the user. A single API is provided to interact with the radio module, so no configuration is required. Unlike open protocols like LoRaWAN, the only way to get and use Sigfox is through the proprietary company.
Architecture
SigFox vs LoRaWAN comparison
| SigFox | LoRaWAN | |
| Frequency | 868/902 MHz (ISM) | 433/868/780/915 MHz (ISM) |
| Urban reach | 3-10 km | 2-5 km |
| Rural reach | 30-50 km | 15-20 km |
| Pack size | 12 bytes | User defined |
Two-way communication
Unlike SigFox, standard LoRa modules can operate bi-directionally. Therefore, LoRa is more suitable for situations where it is necessary to receive and send data from each node.
Data integration
SigFox offers a very simple API to integrate the radio module. Rather, LoRaWAN offers a highly configurable high-level API. Therefore, the integration of LoRaWAN modules is more complicated than that of SigFox modules, but also much more configurable.
Security
Both technologies offer security features. However, only SigFox is capable of identifying and authenticating devices. On the other hand, neither of the two technologies offers encrypted communications.
Conclusions
As we have shown, there are numerous factors to consider when selecting one of these LPWANs that operate on unlicensed spectrum. Some elements to take into account are the bidirectionality and configurability that LoRaWAN offers. On the other hand, the simplicity of integration offered by SigFox together with its greater scope could be discarded elements.
If you liked our article, give it a “like”, comment and share on your social networks. Subscribe to our Newsletter so that you are aware of the latest news. We have a very active Facebook community, very interesting post Instagram and you will find constant activity on our Twitter.




